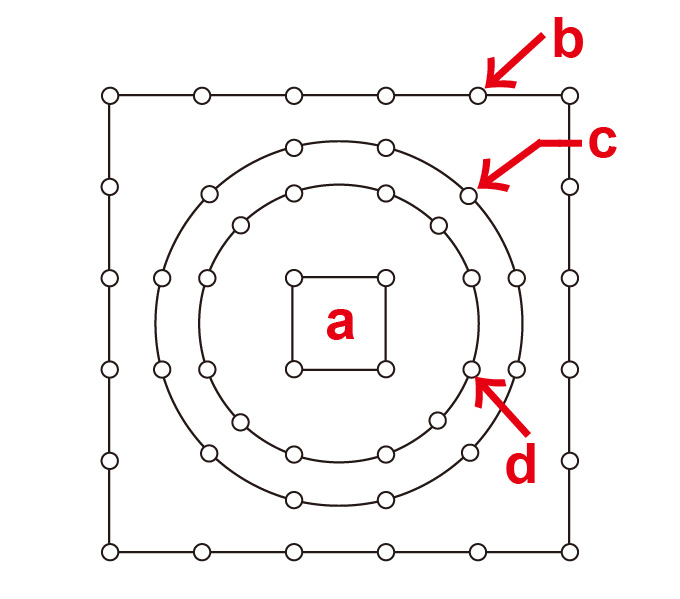
| Suirinbashira are the outer circle of pillars
that divide the exterior pillars from the core *moya
母屋 in a large two-storied type pagoda *tahoutou
多宝塔 with a square first story, cylindrical form above and square pyramidal roof
*hougyou yane 宝形屋根.
If the tahoutou is very large, it is called *daitou
大塔. An example, that has suirinbashira is the Konpon Daitou 根本大塔 (24m
square) at Mt. Kouya 高野, Wakayama prefecture. The Buddhist altar *shumidan 須弥壇 is in the center surrounded by four octagonal pillars, surrounding the altar
area is a circle of moya pillars that separates the core from the outer
aisle formed by the suirinbashira. The suirinbahira corresponds
to the pillars on the perimeter of an ordinary tahoutou. A *mokoshi
裳階, a pent-roofed aisle one bay deep surrounds the pagoda. It has square pillars
that form five-bays on each side. |