|
||
 |
||
@
(C)2001 Japanese Architecture and Art Net Users System.@No reproduction or republication without written permission.
fΪΜeLXgEΚ^ECXgΘΗASΔΜRecΜ³f‘»E]ΪπΦΆά·B
|
||||||
| @ | ||||||
| koshikake kamatsugi@|p | ||||||
| KEY WORD :@architecture / joints | ||||||
| @ | ||||||
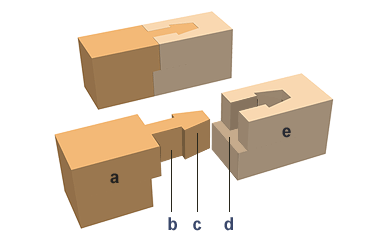
| Also shikimen kamatsugi ~Κp. A half-lap, gooseneck tenon joint. An end joint which combines two joints: a half-lap *koshikaketsugi |p and a gooseneck tenon joint *kamatsugi p. The gooseneck mortise and the bench, or seat, of the lap joint are cut so that the mortise occupies about half the thickness of the timber. The bench made from the remaining half extends like a step beyond the mortise. The second timber@contains the gooseneck tenon; the undercut overlaps the bench when the tenon is dropped into place in the corresponding mortise. If a half-blind mortise, mechigai hozoana ΪαΩΌ, is cut vertically into the center of the bench and a matching tenon is made on the undercut part beneath the dovetail, the combination joint is called koshiire mechigaitsuki kamatsugi όΪαtp. The half blind tenon prevents damage from twisting forces. Koshikake kamatsugi is based on the same principles as *koshikake aritsugi |ap; only the shape of the tenon and mortise differ. Frequently used to join two hidden purlins (roof joints) *nogeta μ , and foundation footings *dodai yδ. | ||||||
| @ | ||||||

|
||||||
@ |
||||||
| REFERENCES: | ||||||
| @ | ||||||
| EXTERNAL LINKS: | ||||||
| @@ | ||||||
| NOTES: | ||||||
| @ | ||||||
(C)2001 Japanese Architecture and Art Net Users System.@No reproduction or republication without written permission. fΪΜeLXgEΚ^ECXgΘΗASΔΜRecΜ³f‘»E]ΪπΦΆά·B |
||||||
| @ |